Glossary
Carbon steels
Carbon steels only contain alloying elements used for steel production, as carbon, manganese, silicon, etc.

Carbon steel, % C = 0.2
| Classification |
|
|
|
Carbon content |
| - Low-carbon steel |
|
|
|
less than 0.30 % C |
| - Medium-carbon steel |
|
|
|
in the range of 0.30 % to 0.60 % C |
| - High-carbon steel |
|
|
|
above 0.60 % C |
Steel Castings
| Classification |
|
|
|
Carbon content |
| - Low-carbon steel castings |
|
|
|
less than 0.20 % C |
| - Medium-carbon steel castings |
|
|
|
in the range of 0.20 % to 0.50 % C |
| - High-carbon steel castings |
|
|
|
above 0.50 % C |
| - Low-alloy steel castings |
|
|
|
total alloy content of less than 8 % |
Low alloy steels
Low alloy steels contain alloying elements as Ni, Mn, Cr, Si, Mo, Nb, Cu.
The percentage of all alloying elements does not exceed 5%.
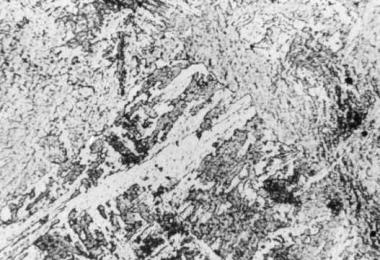
Low alloy steel
High alloy steels
High alloy steels contain alloying elements as Ni, Mn, Cr, Mo, Nb, W, V, Cu.
The total percentage of all alloying elements is higher than 5%.
Stainless steels
Stainless steels are high alloy steels. Their chromium content is at least 12%.
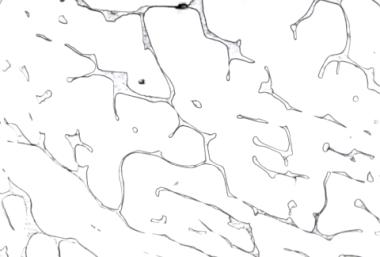
Austenitic steel
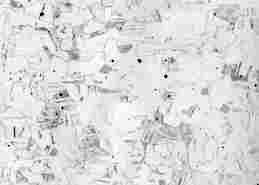
Austenitic steel
Heat resisting steels
Heat resisting steels have good resistance to oxidation as well as high creep strength to about 1000°C. Additions of titanium, aluminium or silicon improve the high temperature characteristics
For further information, on-site training, technical advise or project management, please do not hesitate to
contact us.
|
