Structure of cast iron
The two most important types of cast iron are grey cast iron and spheroidal
graphite cast iron:
Grey cast iron
Structure: Graphite flakes in a iron matrix
Compressive stress: Excellent compressive strength and low elastic modulus
Wear behaviour: The friction coefficient is low (graphite lubrication)
Brittleness: Percentage elongation after fracture is very low, extremely notch
sensitive
Strength: Tensile strength is relatively low ( in function of grade), no yield
point - no overload capacity
Machining / Cutting: Very good machinability for drilling and machining, cannot
be sheared
Oxyacetylene cutting is difficult.
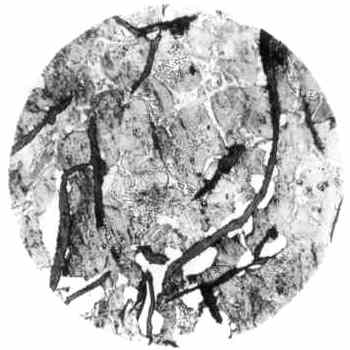
Grey cast iron structure
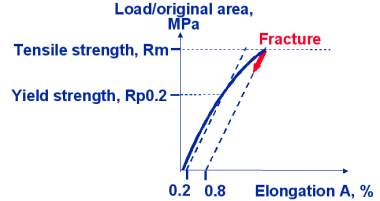
Typical stress elongation curve for grey cast iron
Spheroidal graphite cast iron
Structure: Spheroidal graphite in a iron matrix
Compressive stress: Excellent compressive strength, slightly more elastic than
steel
Wear behaviour: Similar to cast steel
Brittleness: Plastic deformation (percentage elongation) after fracture is much
higher than for grey cast iron
Strength: Tensile strength up to 800 MPa, elastic limit is at least half the
tensile strength
Machining / Cutting: Very good machinability for drilling and machining, cannot
be sheared
Oxyacetylene cutting is difficult.
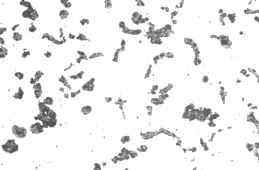
Spheroidal graphite cast iron structure
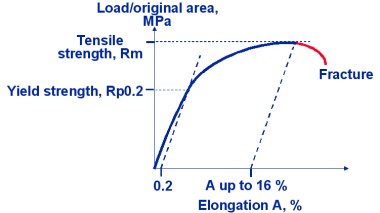
Typical stress elongation curve for spheroidal graphite cast iron
Typical components
Grey cast iron
- Heavy parts in general
- Machine bases
- Gears, heavy gear boxes
- Pulleys, transmission cases
- Housings, casings
- Machine guards
- Engine cylinder blocks and heads
- Furnace parts, moulds, glass moulds
- Cold cropping tools
- Valves, gates, pump bodies
Spheroidal graphite cast iron
- Heavy parts in general
- Machine bases
- Gears, crankshafts
- Pulleys
- Housings, casings
- Machine guards
- Heavy tubes, pipelines, fittings
- Cold cropping tools
- Stamping tools and dies
- Valve and pump bodies (steam, etc.)
For further information, on-site training, technical advise or project management, please do not hesitate to
contact us.
|
